위 파일을 다운받았으면 아래 명령어를 통해 PostgreSQL 데이터베이스를 만들고 테이블을 삽입해준다.
CREATE DATABASE practice1;
\c practice1
\i [filepath]/DDL.sql
\i [filepath]/smallRelationsInsertFile.sql
[Lab 2] Exercise (1)
2-1-1 Find the titles of courses in the Comp. Sci. department that have 3 credits
-> select title from course where dept_name=‘Comp. Sci.’ and credits=3;
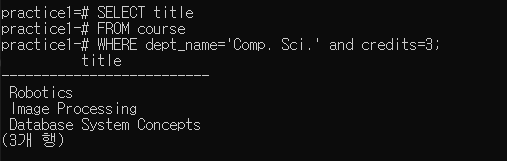
2-1-2 Find the IDs of all students who were taught by an instructor named Srinivasan; make sure there are no duplicates in the result
-> select distinct takes.ID from takes, teaches, instructor where takes.course_id=teaches.course_id and takes.sec_id=teaches.sec_id and takes.year=teaches.year and takes.semester=teaches.semester and instructor.id=teaches.id and instructor.name=‘Srinivasan’;
Primary Key가 5가지 btree 이므로 모두 비교해야한다.
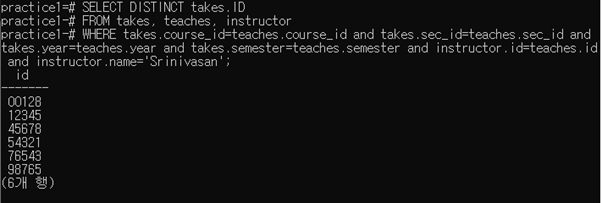
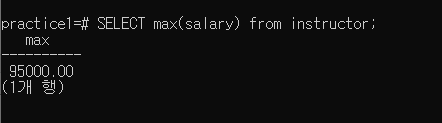
2-1-3 Find the highest salary of any instructor
select max(salary) from instructor;
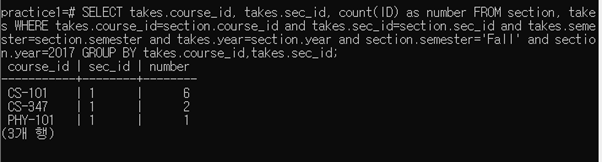
2-1-4 Find the enrollment (i.e. the number of students) for each section that was offered in Fall 2017 (“course_id, section_id, number of students” 가 출력되어야 함)
SELECT takes.course_id, takes.sec_id, count(ID) as number FROM section, takes WHERE takes.course_id=section.course_id and takes.sec_id=section.sec_id and takes.semester=section.semester and takes.year=section.year and section.semester=‘Fall’ and section.year=2017 GROUP BY takes.course_id,takes.sec_id;
[Lab 2] Exercise (2)
create table grade_points(grade varchar(2) primary key, points numeric(2,1));

insert into grade_points values (‘A+’, 4.3), (‘A’, 4.0), (‘A-’, 3.7), (‘B+’, 3.3), (‘B’, 3.0), (‘B-’, 2.7), (‘C+’, 2.3), (‘C’, 2.0), (‘C-’, 1.7), (‘D+’, 1.3), (‘D’, 1.0), (‘D-’, 0.7), (‘F’, 0.0);

2-2-1 Find the total grade-points earned by the student with ID 12345, across all courses taken by the student
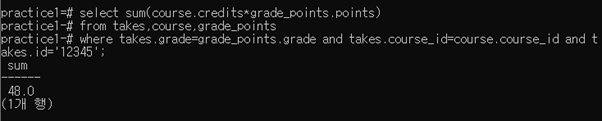
select sum(course.credits*grade_points.points)
from takes,course,grade_points
where takes.grade=grade_points.grade and takes.course_id=course.course_id and takes.id=‘12345’;
2-2-2 Find the grade-point average (GPA) for the above student, that is, the total grade-points divided by the total credits for the associated courses
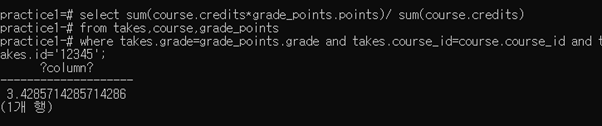
select sum(course.credits*grade_points.points)/ sum(course.credits) from takes,course,grade_points where takes.grade=grade_points.grade and takes.course_id=course.course_id and takes.id=‘12345’;
2-2-3 Find the ID and the grade-points average of every student
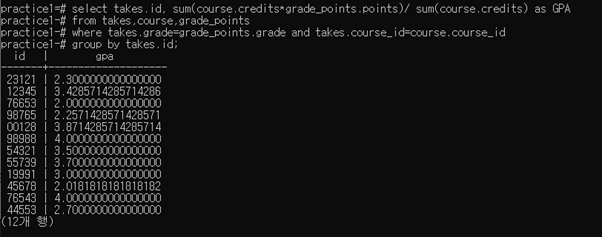
select takes.id, sum(course.credits*grade_points.points)/ sum(course.credits) as gpa
from takes,course,grade_points
where takes.grade=grade_points.grade and takes.course_id=course.course_id
group by takes.id;
2-2-4 Find the ID and the grade-points average of students whose GPA is greater than 3.0
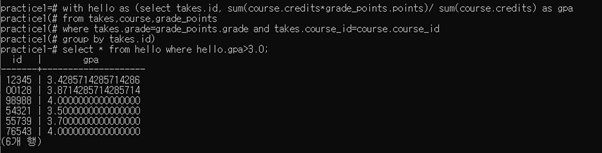
내가 쓴 답: with hello as (select takes.id, sum(course.credits*grade_points.points)/ sum(course.credits) as gpa
from takes,course,grade_points
where takes.grade=grade_points.grade and takes.course_id=course.course_id
group by takes.id)
select * from hello where hello.gpa>3.0;
정답: select takes.id, sum(course.credits*grade_points.points)/ sum(course.credits) as gpa
from takes,course,grade_points
where takes.grade=grade_points.grade and takes.course_id=course.course_id
group by takes.id
having sum(credits * points) / sum(credits) > 3.0;
위 두개의 sql문 결과는 같음
[Lab 3] Exercise (1)
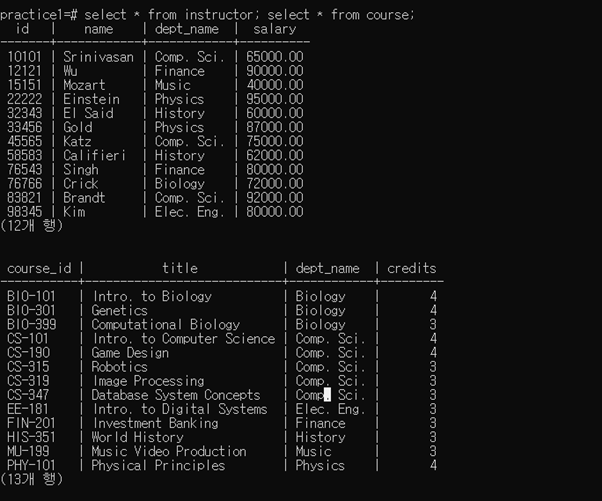
3-1-1 Execute ‘select * from instructor;’ and ‘select * from course;’
3-1-2 Increase the salary of each instructor in the Comp. Sci. department by 10%
update instructor set salary=salary*1.10 where dept_name=‘Comp. Sci.’;
3-1-3 Delete all courses that have never been offered (i.e., do not occur in the section relation)
delete from course where course_id not in (select course_id from section);
3-1-4 Insert every student whose tot_cred attribute is greater than 100 as an instructor in the same department, with a salary of $10,000
insert into instructor
select id,name,dept_name,10000 from student where student.tot_cred>100;
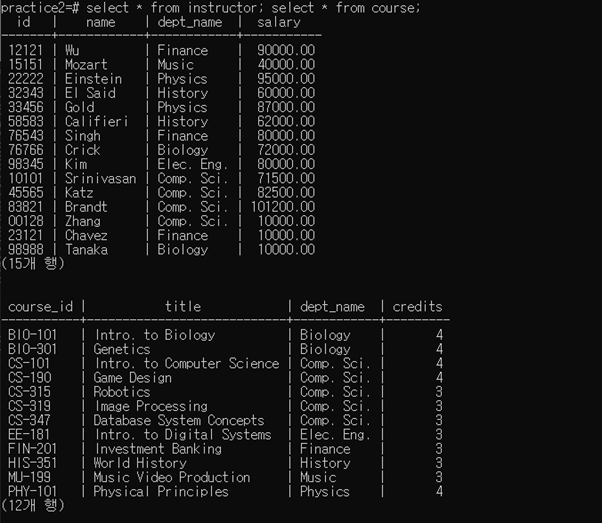
3-1-5 Execute ‘select * from instructor;’ and ‘select * from course;’
아래 그림을 보며 3-1-1에 비해서 instructor은 3개의 행이 늘었고 course 테이블은 1행이 줄었으며 컴퓨터학과 강사들은 salary가 1.10배 늘었고 장학생 3명이 10000달러의 salary와 함께 추가되었다.
[Lab 3] Exercise (2)
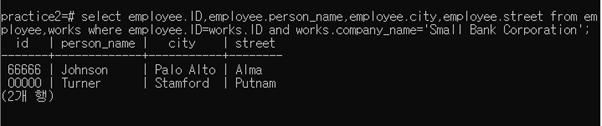
3-2-1 Find the ID, name, city, and street of each employee who works for “Small Bank Corporation”
select employee.ID,employee.person_name,employee.city,employee.street from employee,works where employee.ID=works.ID and works.company_name=‘Small Bank Corporation’;
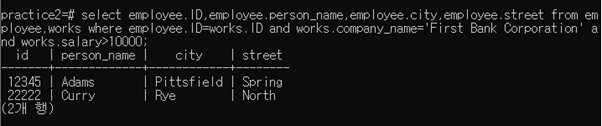
3-2-2 Find the ID, name, city, and street of each employee who works for “First Bank Corporation” and earns more than $10000
select employee.ID,employee.person_name,employee.city,employee.street from employee,works where employee.ID=works.ID and works.company_name=‘First Bank Corporation’ and works.salary>10000;
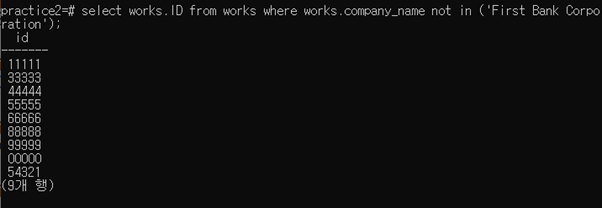
3-2-3 Find the ID of each employee who does not work for “First Bank Corporation”.
select works.ID from works where works.company_name not in (‘First Bank Corporation’);
3-2-4 Find the ID of each employee who earns more than every employee of “Small Bank Corporation”
내가 쓴 답 ->
select works.ID
from employee,works where employee.ID=works.ID and works.salary>(select max(salary) from works where works.company_name=‘Small Bank Corporation’);
정답 ->
select ID
from works
where salary > all(select salary from works where company_name='Small Bank Corporation');
결과는 같음

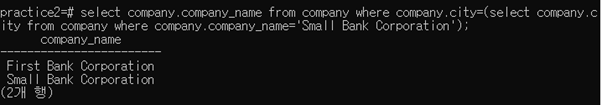
3-2-5 Find the name of each company that is in the city of “Small Bank Corporation” is located
select company.company_name
from company
where company.city in (select company.city from company where company.company_name=‘Small Bank Corporation’);
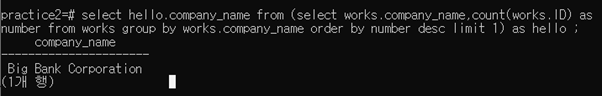
3-2-6 Find the name of the company that has the most employees (or companies, in the case where there is a tie for the most)
내가 쓴 답 ->
select hello.company_name from (select works.company_name,count(works.ID) as number from works group by works.company_name order by number desc limit 1) as hello ;
정답 ->
select company_name
from works
group by company_name
having count (distinct id) >= all (select count (distinct ID) from works group by company_name);
결과는 같음
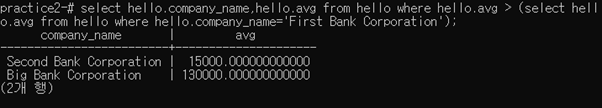
3-2-7 Find the name of each company whose employees earn a higher salary, on average, than the average salary at “First Bank Corporation”
내가 쓴 답 ->
with hello(company_name,avg) as
(select works.company_name,avg(salary) from works group by works.company_name)
select hello.company_name,hello.avg from hello where hello.avg > (select hello.avg from hello where hello.company_name='First Bank Corporation');
정답 ->
select company_name
from works
group by company_name
having avg (salary) > (select avg(salary) from works where company_name = 'First Bank Corporation');
결과는 같음
[Lab 2] Practice
1. Set up integrity constraints, and then execute SQL statements violating them
primary key constraint
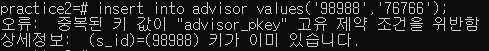
foreign key constraint

not null constraint

2. Make two or more concurrently executed transactions, and show they are executed in an isolated manner
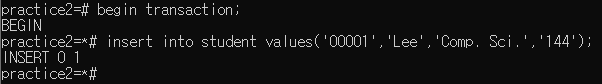
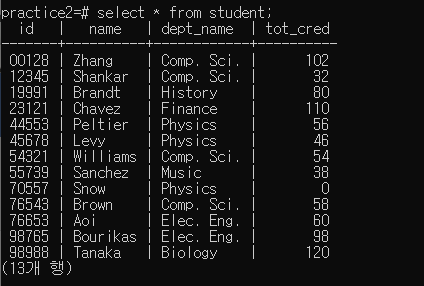
위 그림과 같이 트랜섹션 상태에서 insert를 수행하고 select 문으로 데이터를 확인하면 명령어가 아직 적용이 안된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
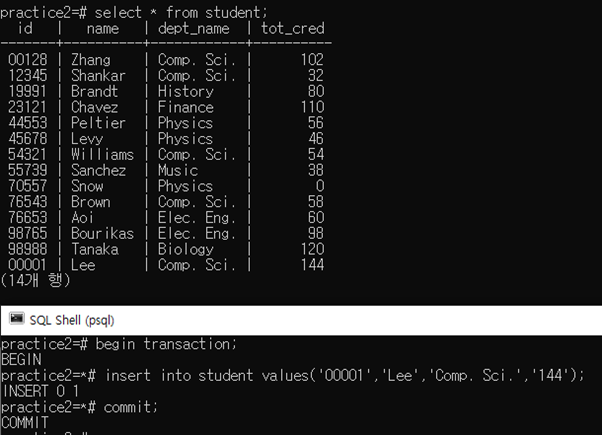
commit을 수행하고 다시 select문을 확인하면 데이터가 수정된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
3. Make users and set up a few authorization rules; Show some nonauthorized accesses
사용자 계정 만들기
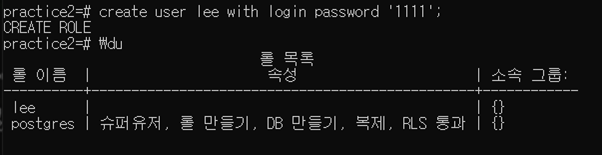
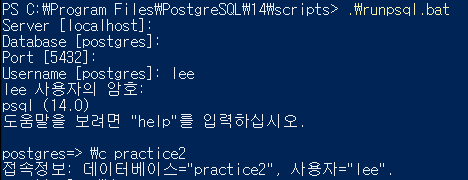
lee 계정으로 psql 실행
advisor 테이블에 대한 권한 없음

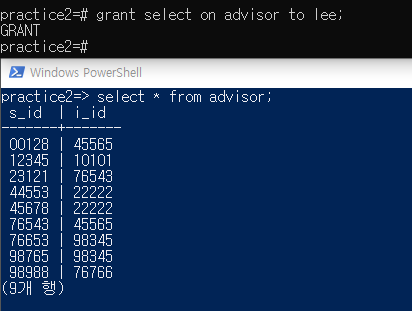
위 그림과 같이 grant로 권한을 주면 lee 계정에서 advisor 테이블 접근 가능
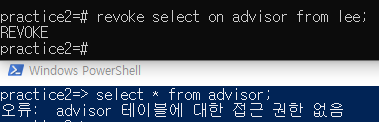
revoke로 다시 권한을 뺏을 수 있다.
4. Create some views and show how view maintenance works and how view update is processed
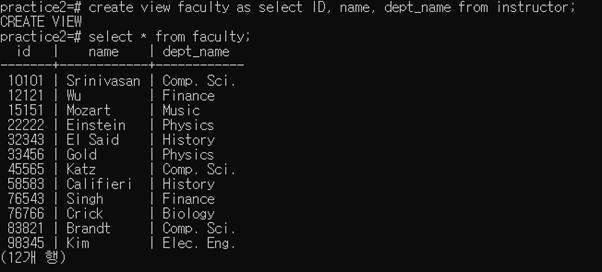
위 그림과 같이 view를 생성할 수 있다.


위 명령어를 각각 수행하고 테이블과 view를 확인해보면 view를 업데이트 하는 것과 테이블을 업데이트 하는 것과 둘 다 똑같이 동작하는 것을 알 수 있다.
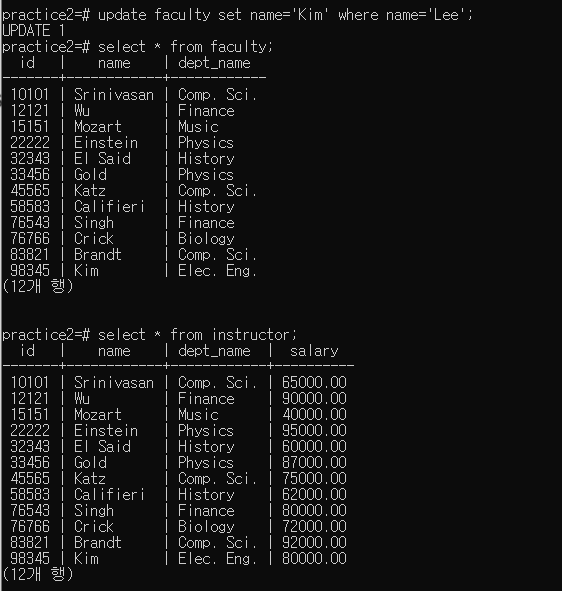
위에서 설명한대로 view를 업데이트하면 테이블도 함께 수정되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
'잡동사니' 카테고리의 다른 글
| CPU 프로세스 우선순위 변경에 따른 CPU 실제사용시간 비교 (0) | 2021.11.03 |
|---|---|
| [리눅스] 파일시스템 관련 명령어 모음 (0) | 2021.10.11 |
| 하드디스크, RAM, ROM, SSD 개념 (0) | 2021.10.05 |
| git 버전별로 컴파일 후 패치된 취약점 확인과정 (0) | 2021.10.02 |
| [운영체제 개념] (0) | 2021.10.01 |




댓글